Today we will covered about Bar Chart in android using aChartEngine. To make the bar graph in android, first you have to download the achartengine.jar from code.google.com/p/achartengine/downloads/list. After successfully downloaded the jar file, put that jar file in your libs folder of your android structure. Now take the following step
Step 1:-
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.graphdemo"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0" >
<uses-sdk
android:minSdkVersion="8"
android:targetSdkVersion="17" />
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme" >
<activity
android:name="com.example.graphdemo.GraphActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<!—Add this activity in your AndroidManifest file -->
<activity android:name="org.achartengine.GraphicalActivity"/>
</application>
</manifest>
Step 2:- activity_graph.xml in res folder
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/BarGraph"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="BarGraph" />
</LinearLayout>
Step 3:- GraphActivity.java
package com.arpit.graphdemo;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
public class GraphActivity extends Activity implements OnClickListener {
Button barGraph;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_graph);
barGraph = (Button) findViewById(R.id.BarGraph);
barGraph.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
switch(v.getId()){
case R.id.BarGraph:
BarGraph bar = new BarGraph();
Intent barIntent = bar.getIntent(this);
startActivity(barIntent);
break;
}
}
}
Step 4: Create a class BarGraph.java
This will be the class where the graph is actually created by using methods of achartengine library.
package com.arpit.graphdemo;
import org.achartengine.ChartFactory;
import org.achartengine.chart.BarChart.Type;
import org.achartengine.model.CategorySeries;
import org.achartengine.model.XYMultipleSeriesDataset;
import org.achartengine.renderer.XYMultipleSeriesRenderer;
import org.achartengine.renderer.XYSeriesRenderer;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.graphics.Color;
public class BarGraph {
public Intent getIntent(Context context){
int y[] = {25,10,15,20};
CategorySeries series = new CategorySeries("Bar1");
for(int i=0; i < y.length; i++){
series.add("Bar"+(i+1),y[i]);
}
XYMultipleSeriesDataset dataSet = new XYMultipleSeriesDataset(); // collection of series under one object.,there could any
dataSet.addSeries(series.toXYSeries()); // number of series
//customization of the chart
XYSeriesRenderer renderer = new XYSeriesRenderer(); // one renderer for one series
renderer.setColor(Color.RED);
renderer.setDisplayChartValues(true);
renderer.setChartValuesSpacing((float) 5.5d);
renderer.setLineWidth((float) 10.5d);
XYMultipleSeriesRenderer mRenderer = new XYMultipleSeriesRenderer(); // collection multiple values for one renderer or series
mRenderer.addSeriesRenderer(renderer);
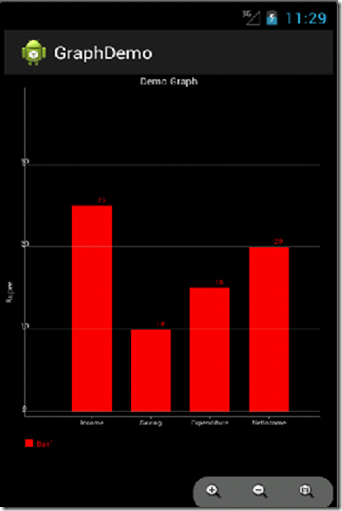
mRenderer.setChartTitle("Demo Graph");
// mRenderer.setXTitle("xValues");
mRenderer.setYTitle("Rupee");
mRenderer.setZoomButtonsVisible(true); mRenderer.setShowLegend(true);
mRenderer.setShowGridX(true); // this will show the grid in graph
mRenderer.setShowGridY(true);
// mRenderer.setAntialiasing(true);
mRenderer.setBarSpacing(.5); // adding spacing between the line or stacks
mRenderer.setApplyBackgroundColor(true);
mRenderer.setBackgroundColor(Color.BLACK);
mRenderer.setXAxisMin(0);
// mRenderer.setYAxisMin(.5);
mRenderer.setXAxisMax(5);
mRenderer.setYAxisMax(50);
//
mRenderer.setXLabels(0);
mRenderer.addXTextLabel(1,"Income");
mRenderer.addXTextLabel(2,"Saving");
mRenderer.addXTextLabel(3,"Expenditure");
mRenderer.addXTextLabel(4,"NetIncome");
mRenderer.setPanEnabled(true, true); // will fix the chart position
Intent intent = ChartFactory.getBarChartIntent(context, dataSet, mRenderer,Type.DEFAULT);
return intent;
}
}
Step 1:-
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.graphdemo"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0" >
<uses-sdk
android:minSdkVersion="8"
android:targetSdkVersion="17" />
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme" >
<activity
android:name="com.example.graphdemo.GraphActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<!—Add this activity in your AndroidManifest file -->
<activity android:name="org.achartengine.GraphicalActivity"/>
</application>
</manifest>
Step 2:- activity_graph.xml in res folder
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/BarGraph"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="BarGraph" />
</LinearLayout>
Step 3:- GraphActivity.java
package com.arpit.graphdemo;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
public class GraphActivity extends Activity implements OnClickListener {
Button barGraph;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_graph);
barGraph = (Button) findViewById(R.id.BarGraph);
barGraph.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
switch(v.getId()){
case R.id.BarGraph:
BarGraph bar = new BarGraph();
Intent barIntent = bar.getIntent(this);
startActivity(barIntent);
break;
}
}
}
Step 4: Create a class BarGraph.java
This will be the class where the graph is actually created by using methods of achartengine library.
package com.arpit.graphdemo;
import org.achartengine.ChartFactory;
import org.achartengine.chart.BarChart.Type;
import org.achartengine.model.CategorySeries;
import org.achartengine.model.XYMultipleSeriesDataset;
import org.achartengine.renderer.XYMultipleSeriesRenderer;
import org.achartengine.renderer.XYSeriesRenderer;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.graphics.Color;
public class BarGraph {
public Intent getIntent(Context context){
int y[] = {25,10,15,20};
CategorySeries series = new CategorySeries("Bar1");
for(int i=0; i < y.length; i++){
series.add("Bar"+(i+1),y[i]);
}
XYMultipleSeriesDataset dataSet = new XYMultipleSeriesDataset(); // collection of series under one object.,there could any
dataSet.addSeries(series.toXYSeries()); // number of series
//customization of the chart
XYSeriesRenderer renderer = new XYSeriesRenderer(); // one renderer for one series
renderer.setColor(Color.RED);
renderer.setDisplayChartValues(true);
renderer.setChartValuesSpacing((float) 5.5d);
renderer.setLineWidth((float) 10.5d);
XYMultipleSeriesRenderer mRenderer = new XYMultipleSeriesRenderer(); // collection multiple values for one renderer or series
mRenderer.addSeriesRenderer(renderer);
mRenderer.setChartTitle("Demo Graph");
// mRenderer.setXTitle("xValues");
mRenderer.setYTitle("Rupee");
mRenderer.setZoomButtonsVisible(true); mRenderer.setShowLegend(true);
mRenderer.setShowGridX(true); // this will show the grid in graph
mRenderer.setShowGridY(true);
// mRenderer.setAntialiasing(true);
mRenderer.setBarSpacing(.5); // adding spacing between the line or stacks
mRenderer.setApplyBackgroundColor(true);
mRenderer.setBackgroundColor(Color.BLACK);
mRenderer.setXAxisMin(0);
// mRenderer.setYAxisMin(.5);
mRenderer.setXAxisMax(5);
mRenderer.setYAxisMax(50);
//
mRenderer.setXLabels(0);
mRenderer.addXTextLabel(1,"Income");
mRenderer.addXTextLabel(2,"Saving");
mRenderer.addXTextLabel(3,"Expenditure");
mRenderer.addXTextLabel(4,"NetIncome");
mRenderer.setPanEnabled(true, true); // will fix the chart position
Intent intent = ChartFactory.getBarChartIntent(context, dataSet, mRenderer,Type.DEFAULT);
return intent;
}
}

Technorati Tags: android bar chart,charts in android,achartengine android,achartengine,bar graph android




0 comments:
Post a Comment